What's The Difference Between An FPV Drone And A Normal One?
First-Person View (FPV) drones and normal drones, often referred to as consumer drones, differ primarily in their design, purpose, piloting experience, and applications. Here are the key differences between FPV drones and normal drones:
1. Piloting Experience
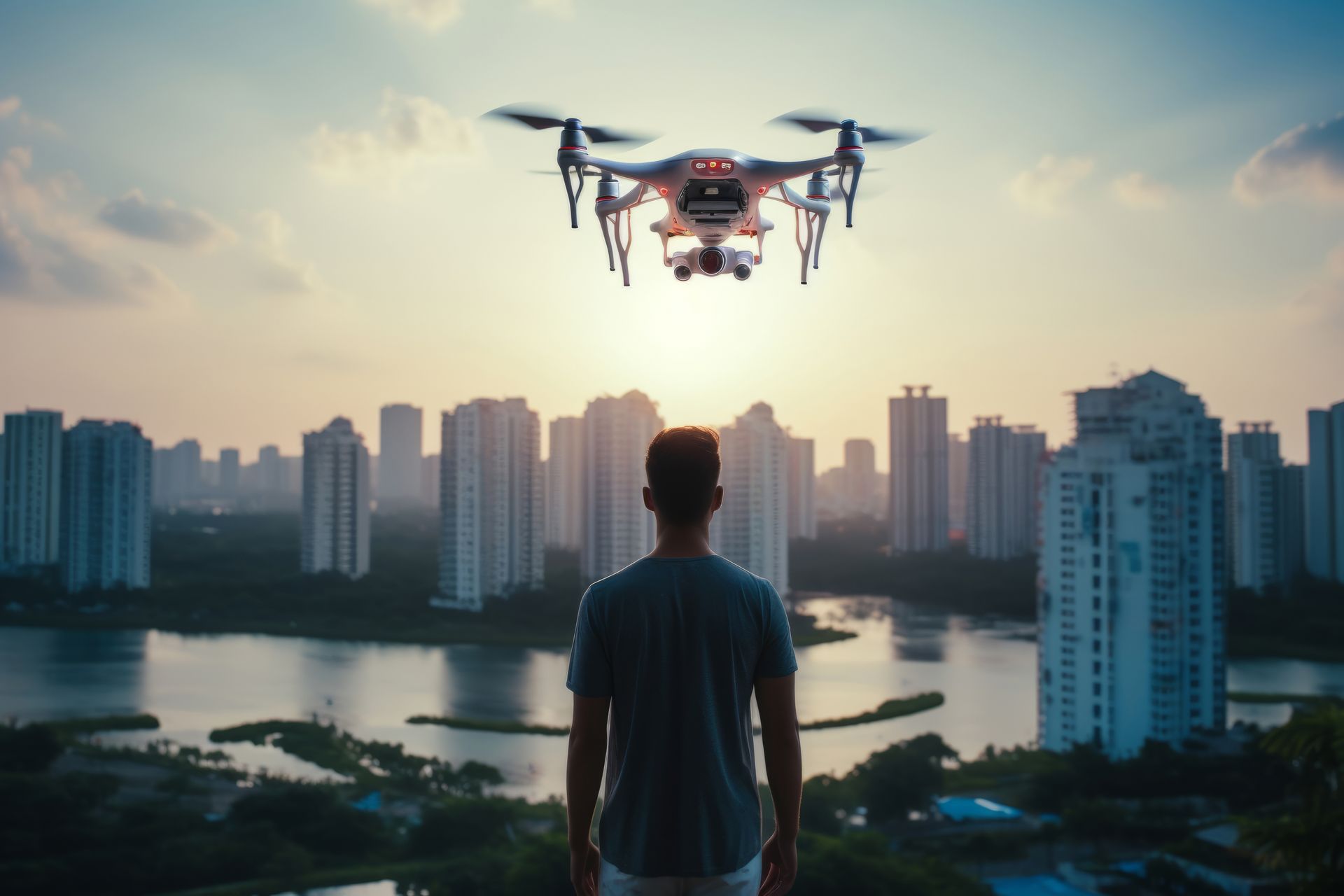
Normal Drones: Pilots operate normal drones by visually observing the drone from the ground while controlling it with a remote controller. They rely on the drone's camera feed displayed on a screen to navigate and frame shots.
FPV Drones: FPV drones provide a real-time video feed directly to specialised goggles or a monitor worn by the pilot. This gives the pilot a first-person perspective, as if they are sitting inside the drone and flying it.
2. Viewing Perspective
Normal Drones: Pilots have an external perspective of the drone's flight. They observe the drone and its surroundings from a third-person view.
FPV Drones: Pilots experience a first-person view, seeing exactly what the drone's camera sees. This immersive perspective enhances the sense of flight and speed.
3. Control and Manoeuvrability
Normal Drones: Pilots control normal drones using the remote controller, which provides a traditional flight experience with the drone visible from the ground.
FPV Drones: FPV drones are often built for agility and speed, allowing pilots to perform intricate manoeuvres and fly through challenging obstacles with precision due to the first-person perspective.
4. Design and Build
Normal Drones: Consumer drones are typically designed for ease of use, stability, and versatility. They often come with built-in cameras for photography and videography, and they prioritize flight time and stability.
FPV Drones: FPV drones are often customized or purpose-built by hobbyists and enthusiasts. They are lightweight, agile, and designed for speed and manoeuvrability to provide an exhilarating flying experience.
5. Purpose and Applications
Normal Drones: Consumer drones are used for various applications, including aerial photography, videography, surveying, mapping, recreational flying, and more. They are versatile and cater to a broad range of users.
FPV Drones: FPV drones are popular for racing, freestyle flying, and acrobatics, providing an adrenaline-pumping experience for hobbyists and professional pilots. They are also used for cinematic FPV shots in filmmaking.
6. Learning Curve
Normal Drones: Consumer drones are generally easier to learn and fly, making them accessible to beginners and those new to flying drones.
FPV Drones: Flying FPV drones requires a steeper learning curve due to the immersive and fast-paced experience. Pilots need practice to master the controls and maintain orientation.
In summary, FPV drones offer a more immersive and thrilling flying experience, providing a first-person view through specialised goggles. On the other hand, normal drones are versatile and accessible, often used for various applications like photography, videography, and recreational flying with a third-person view. Each type of drone caters to different preferences, skill levels, and intended uses.